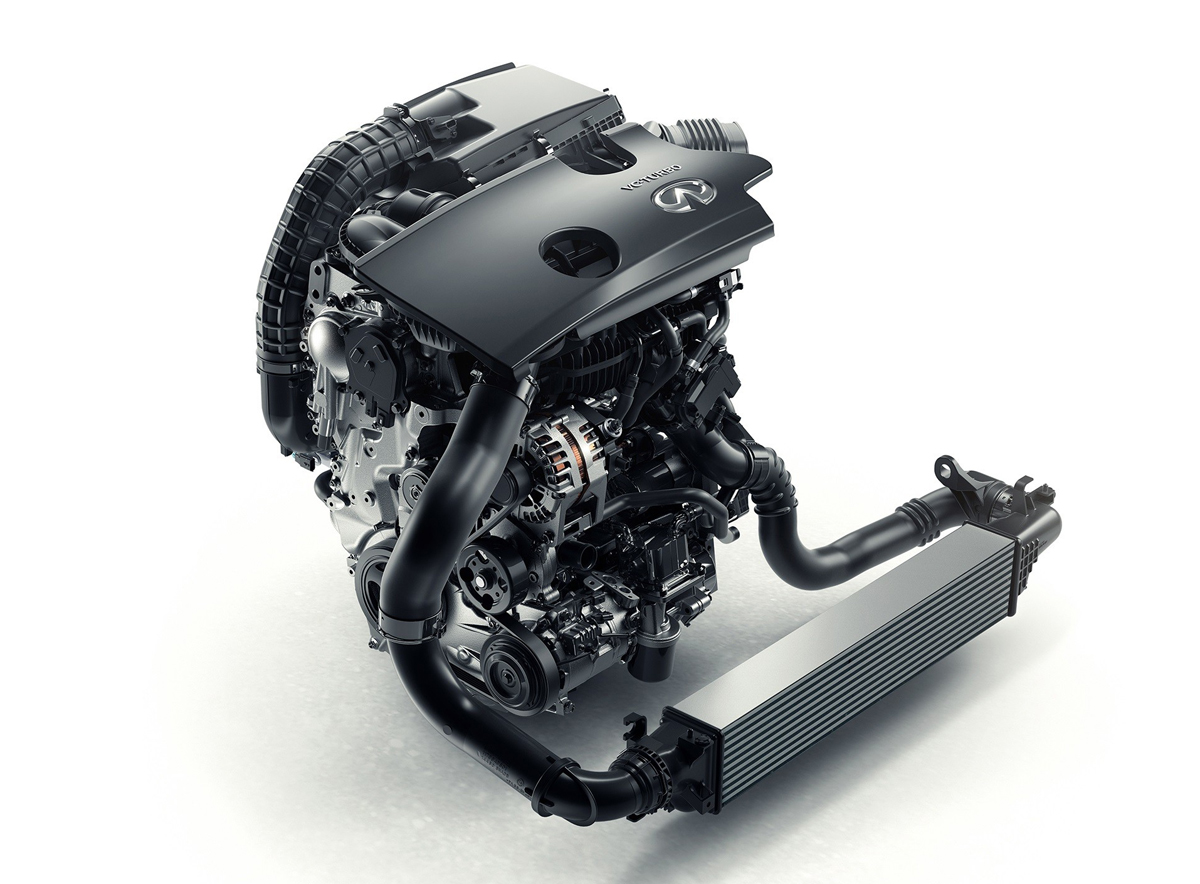
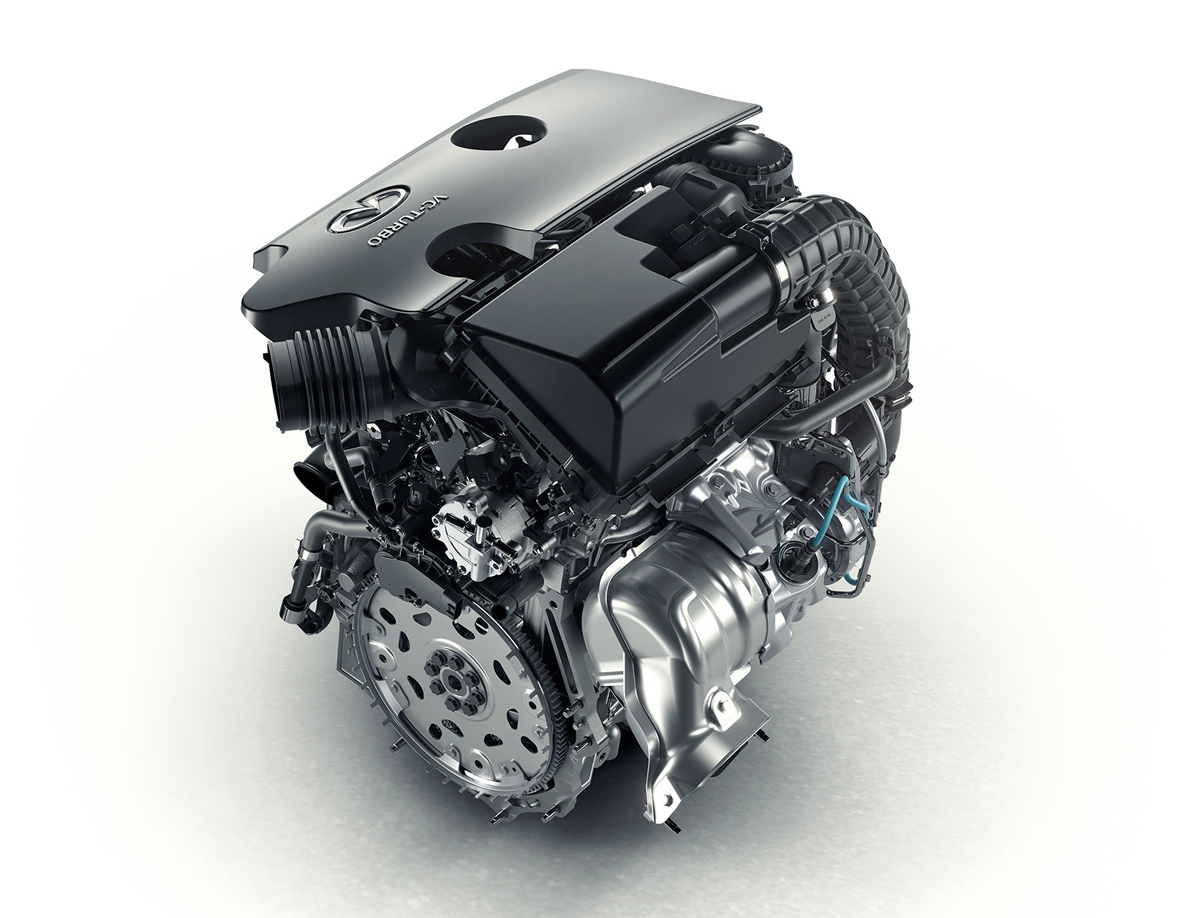
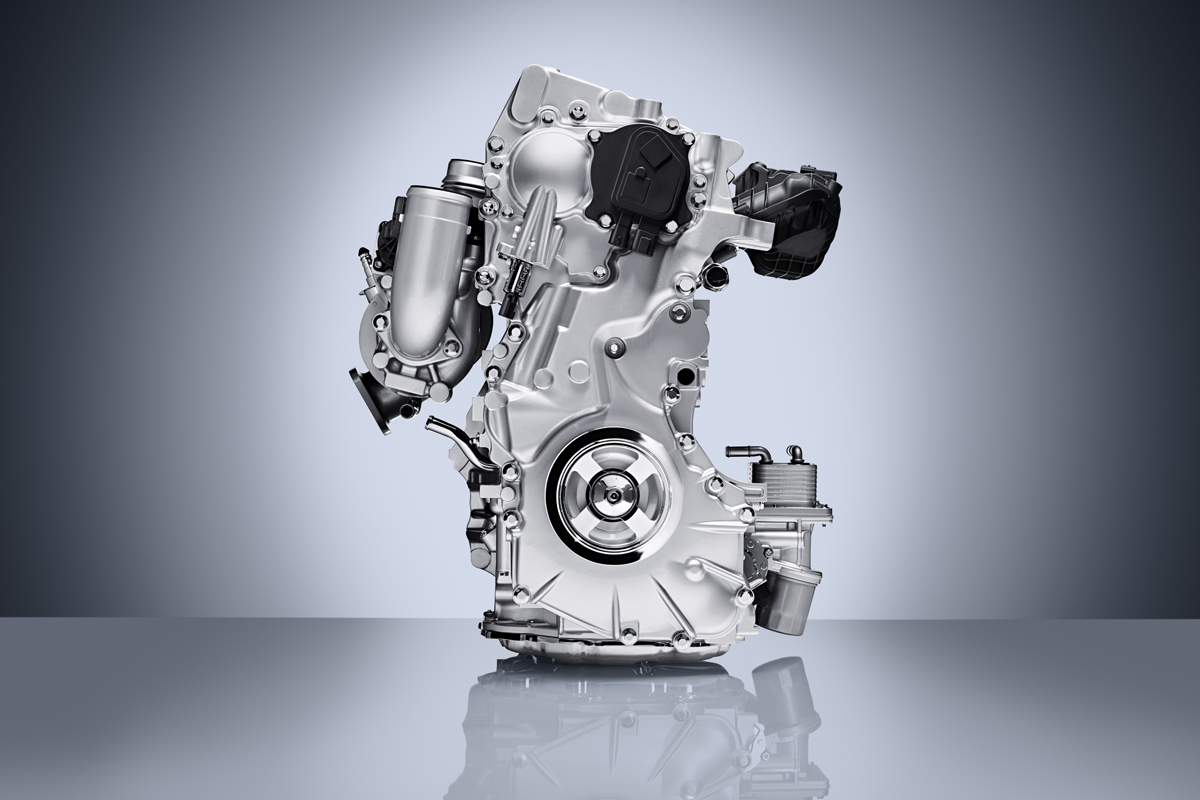
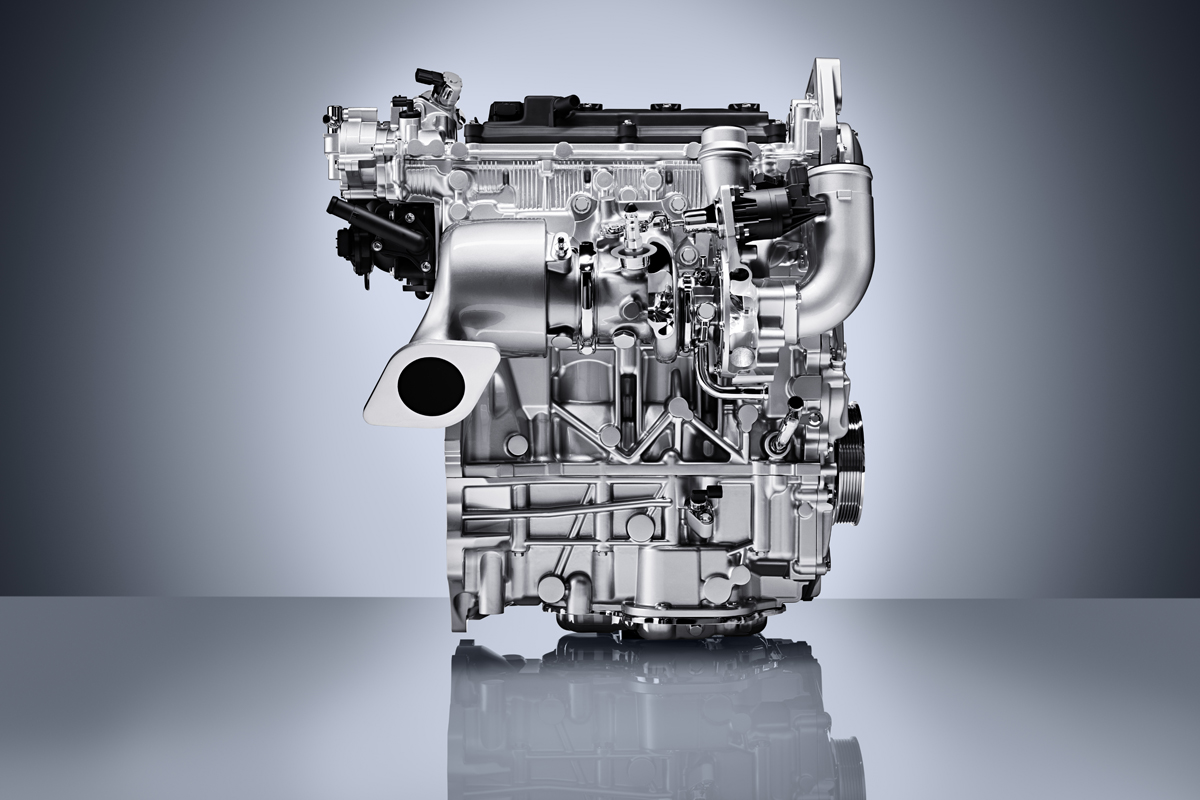
While it made little news, likely one of the biggest innovations in the history of the internal combustion engine has come in 2016 with Infiniti’s announcement of their 2.0-liter variable compression turbo (VC Turbo) engine.
In the past couple decades, the internal combustion engine has seen dramatic developments from variable valve timing to direct fuel injection, and the mass adoption of turbochargers all to raise horsepower and efficiency at the same time.
One of the last frontiers however has been the dream to create an engine with a variable compression ratio that allowed for infinite tuning and operation ranges instead of settling for a compromise of fixed compression.
This year in Paris, Infiniti shocked the industry with they unveiled their all all-new 2.0-liter VC Turbo gasoline four-cylinder engine that realizes this dream, offering a continuously variable compression ratio spread from 8:1 to 14:1.
Why? Higher compression ratios offer better efficiency but not always more power. Lower compression ratios allow for greater turbo boost and more aggressive fuel to air ratios for more power when it’s wanted. It’s having the best of both worlds in the same engine.
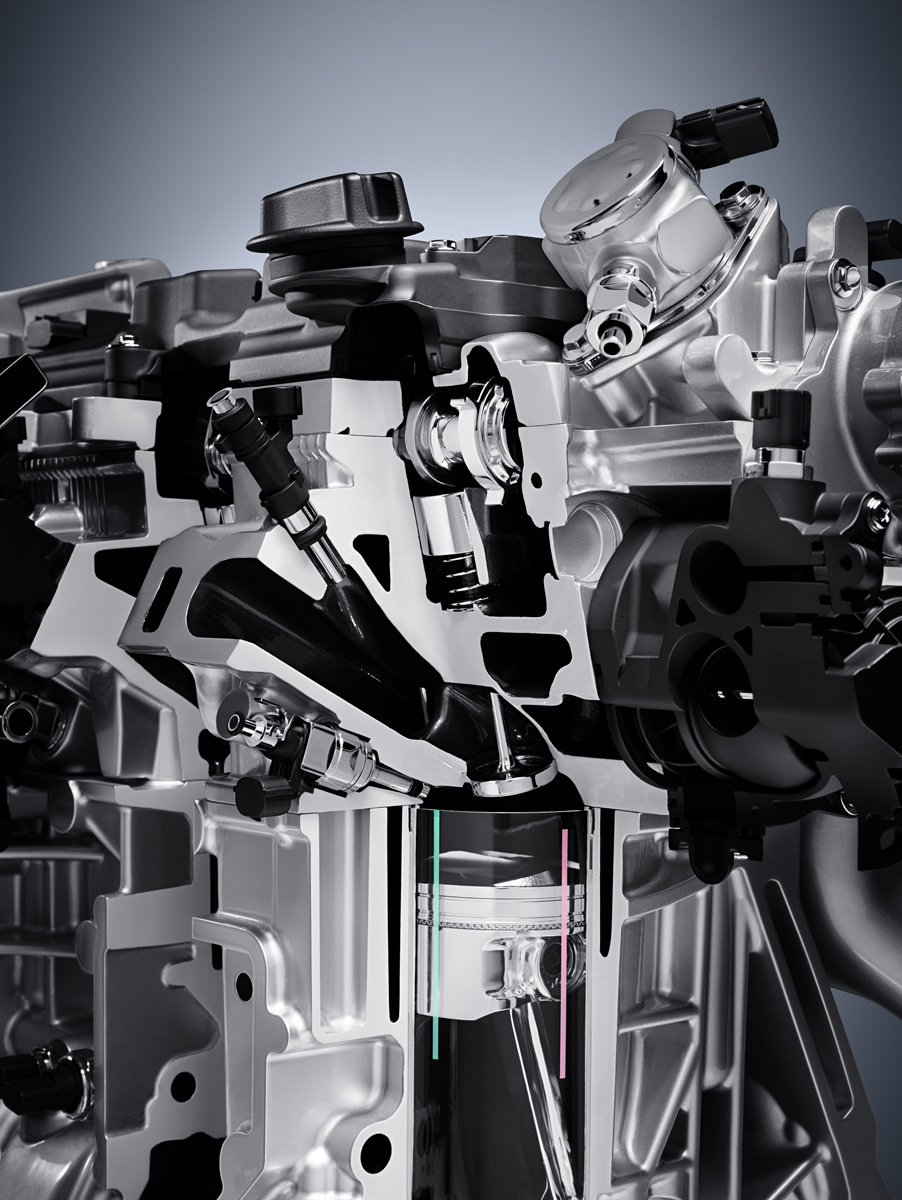
The VC Turbo starts out with all the latest technologies that exist. You have both direct and port fuel injection to use either or both when they are best suited – horsepower or efficiency. There’s variable cam timing too that has a wide-range allowing for both an Atkinson or Otto combustion cycles.
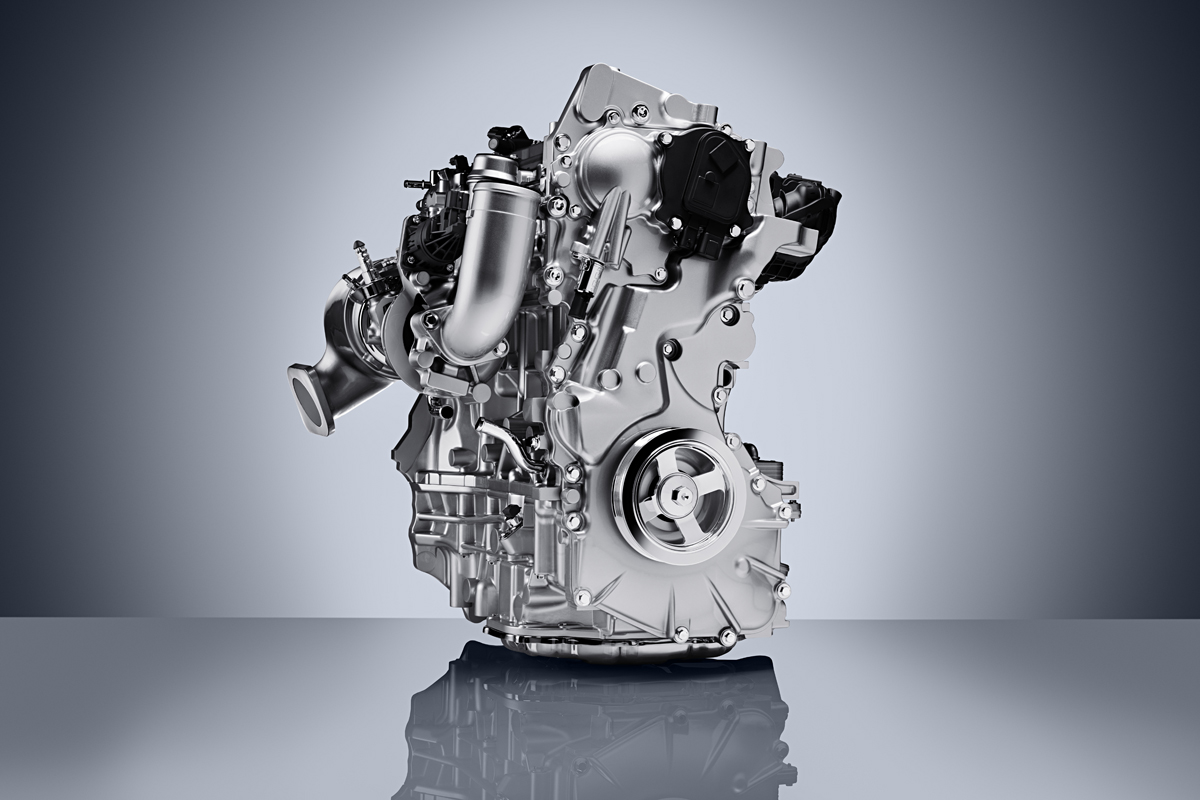
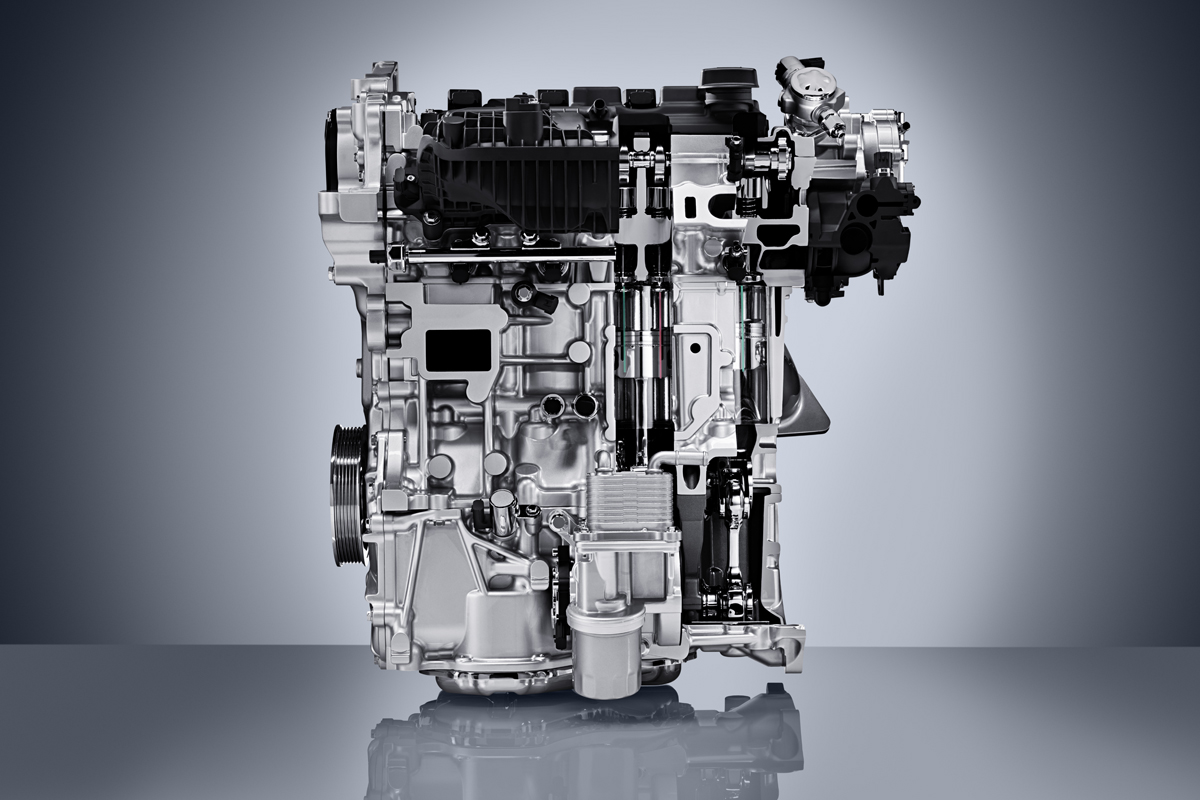
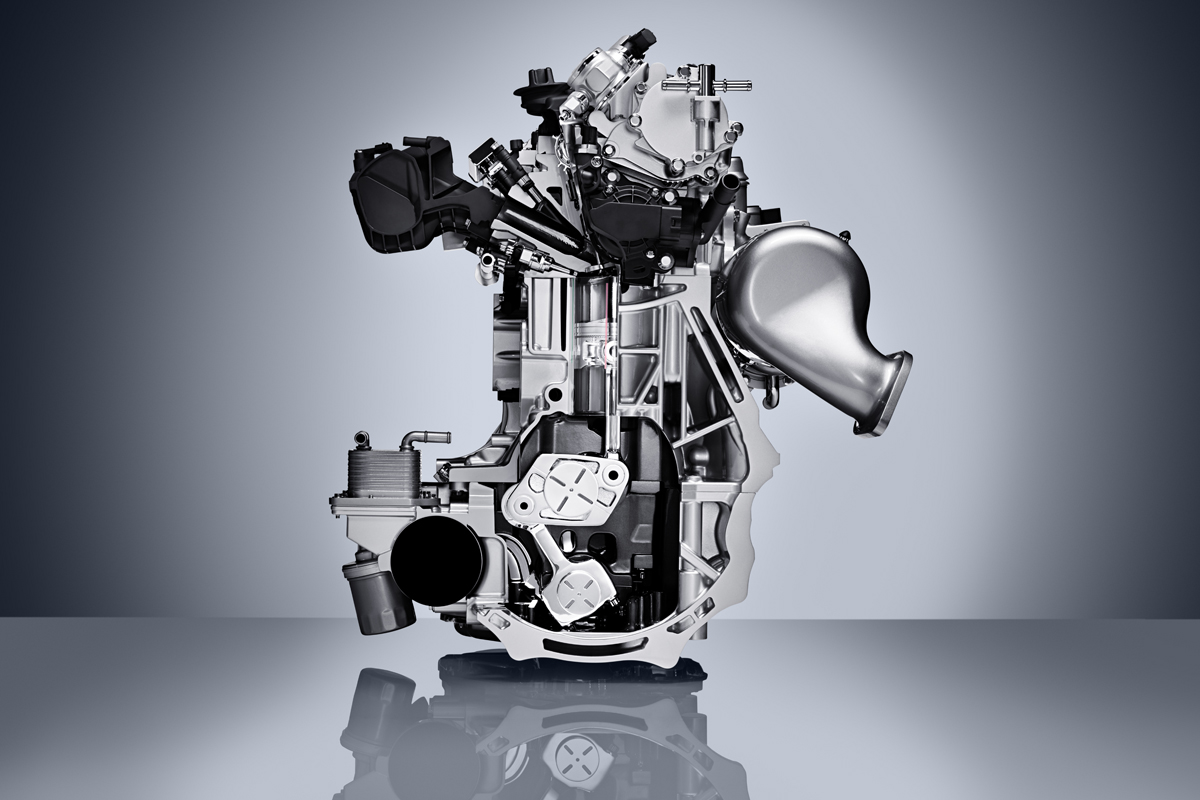
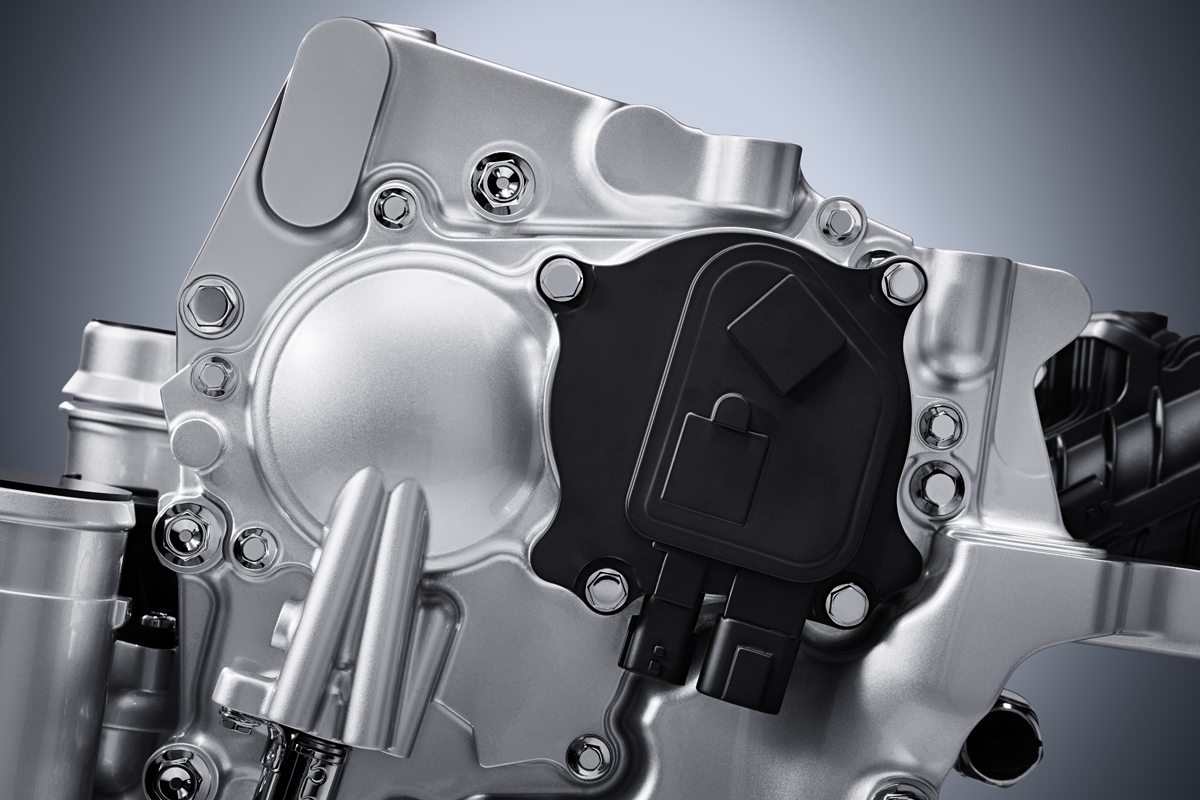
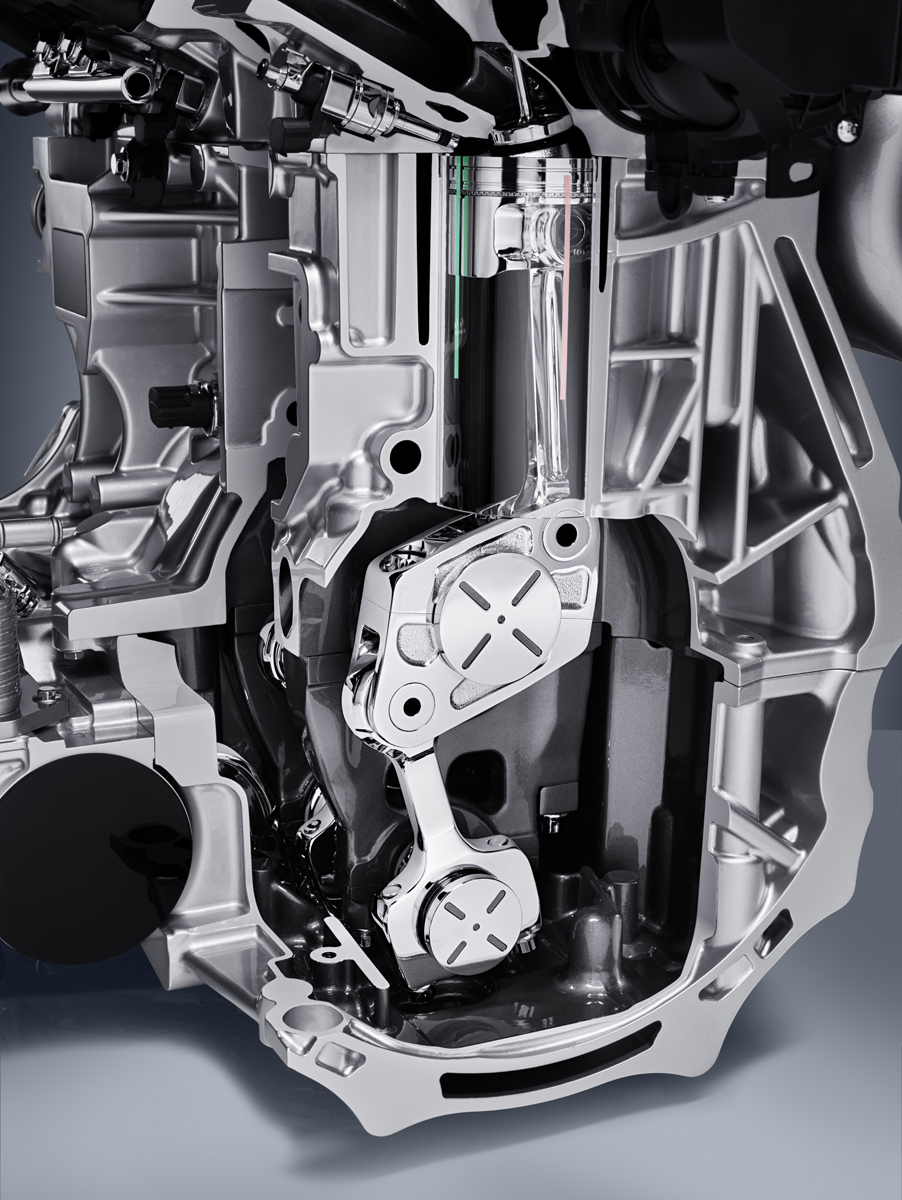
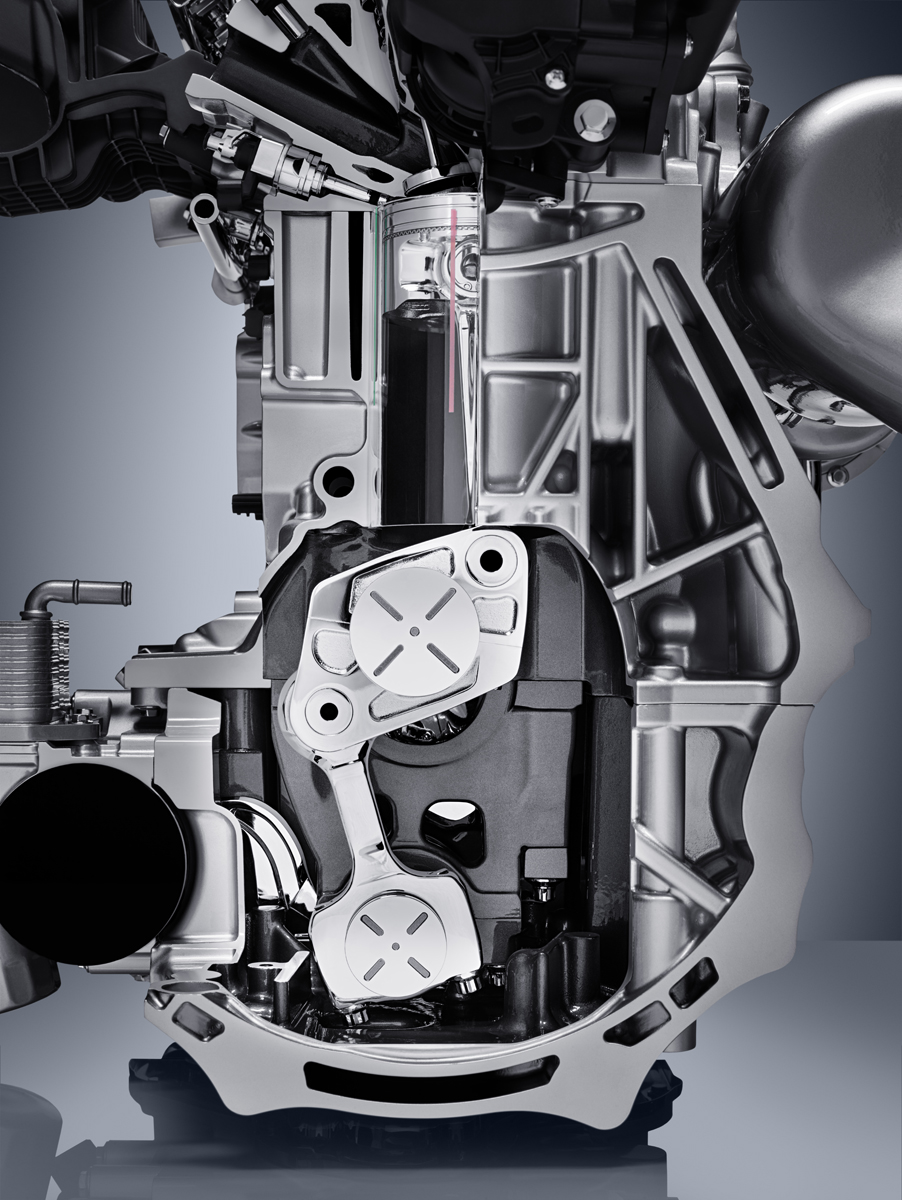
What makes the VC Turbo completely different however is its multi-link control system buried deep below the crankshaft that allows the piston stroke to be raised and lowered continuously depending on driver inputs and load conditions.
The crankshaft itself is offset from the axis of the cylinder bores. Below, a harmonic drive reduction gear turns an eccentric control shaft connected to the multi-link that effectively adjusts the rotational axis for all four of the cylinders piston connecting rods up and down.
By moving the axis of the stroke up and down, compression ratio and by extension displacement can be varied continuously. In this case, the displacement itself ranges from 1997 to 1970 cc and as said the compression ratio from 8:1 to 14:1.
Because the crankshaft is offset from the cylinder bores, the piston rod is in a near vertical position for the combustion stroke and has less lateral movement which fosters smoother and quieter operation than most four-cylinder engines. They were even able to eliminate balance shafts as they weren’t needed.
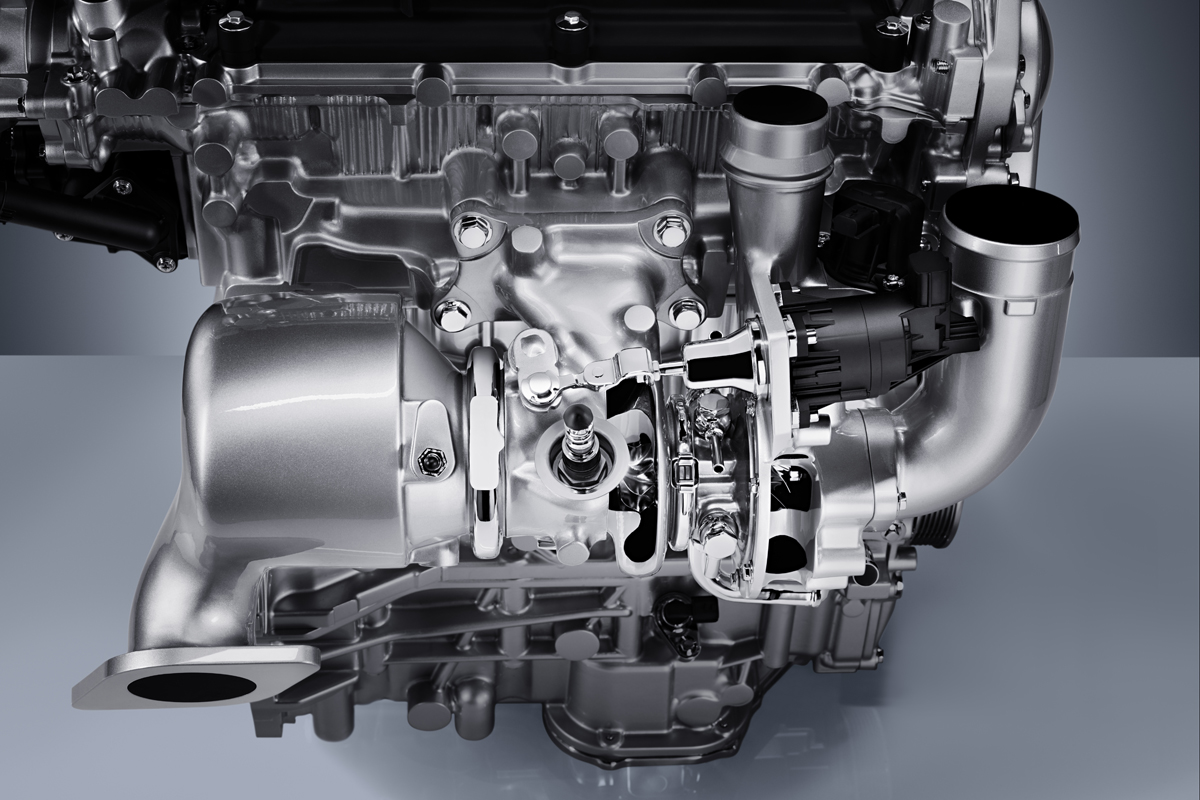
Packaging too has been streamlined with an integrated exhaust manifold, allowing the single-scroll turbocharger to bolt directly to the head. The catalytic converter can then be mounted directly to the turbocharger, further enhancing thermal efficiencies.
This is all good, fuel economy and reduced emissions but what about power? Infiniti says on this first production engine we will see in 2018 we can expect 268 horsepower and 288 pound feet of torque. This comes with some 27% better fuel efficiency than in a similarly powered V6 says Infiniti.
Will it be durable? Infiniti has been working on this design since 1996 with over 100 prototypes in the twenty year process. With over 30,000 hours and nearly 2,000,000 miles of testing done, they are confident it’s ready for prime time and will be the first to market with a variable compression engine.
While Infiniti hasn’t yet said which models will receive the new VC Turbo engine we can expect in time virtually all of the vehicles that offer the current 2.0-liter turbocharged engine to be a candidate from the new QX30 to the Q50, the Q60 and even mid-size crossover SUVs just to start.
Technical specifications:
Engine: ‘MR20 DDT’ 2.0-liter VC Turbo
Construction: Aluminum block with arc-sprayed mirror coating to cylinder bores, aluminum cylinder head with integrated exhaust manifold, single-scroll turbo with intercooler
Compression ratio: 8.0:1 ~ 14.0:1
Capacity: 2.0-liters, 1,997 ~ 1,970 cc
Bore x Stroke: 84.0 x 94.1
Intake cam: Electronic Variable Valve Timing Control
Exhaust cam: Hydraulic Variable Valve Timing Control
Turbocharger: Single-scroll turbocharger with electronic wastegate actuator
Fuel system: Gasoline direct injection (DIG) and/or multi-point injection (MPI)
Max power: 268 hp
Max torque: 288 lb ft